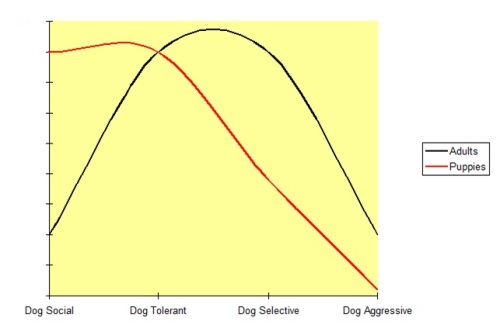
This post, written by the brilliant Bailey Stickney and reposted with permission from her blog, contains three examples where giving up some control was a better solution than exerting control over a situation.

1. My cat used to race into the garage any time the opportunity arose.
There are a lot of hiding places for a cat in my garage, and things aren’t stored in there very safely. There are boxes stacked precariously, and I worry they could fall and crush him. When we first moved in here, there were leftover chemicals and other stuff from the previous owners that I was intensely worried about.
Because he is a normal, curious cat, and the garage was off-limits for him, he would race in there any chance he got. And he did not want to come out. He refused to be found. The harder we tried to get him to come out, the deeper he’d hide.
Some years have gone by, and I am a better trainer now. My garage is still a mess, but it is a bit safer, and I don’t feel as desperate to keep him out of there. I’ve given up the idea of tightly controlling this cat, and it has paid off!
I don’t try to block his access to that garage anymore. When he goes in, I don’t make it a big deal at all. When he comes out he gets a great treat. Now he doesn’t really care about going in the garage anymore. When he does go in the garage, he goes in with me, and follows me out when I leave. And then he gets his treat. A small price to pay for safety.
The same thing happened with the yard. I used to really worry about him running away (because he did run away one time) Again, I tried to block his access to the yard, but that just made him try harder, and he refused to be caught when he did get out. Now I let him go out if he chooses, and I just reward him handsomely when he comes in. I also reward him every time the door opens; he gets a treat every time I let the dogs out. These days, if the door is open, he may dash outside, but his main goal is to immediately dash back inside. It is really quite funny – he’s not trying to get outside, he’s trying to come back inside so that he can get a treat!
I had to give up my perception of control in order to gain actual control of my cat.
—-
2. I’m not one to say that owners and humans cause a lot of behavior problems, but resource guarding is one area where we tend to make it worse.
We’ll see this often in gun dogs (retrievers, pointers, spaniels, setters, etc.). These dogs naturally like to have things in their mouths. And they are dogs, so they like to put gross things in their mouths. Things like dirty underwear and dirty socks. Humans usually don’t like this because it’s gross, and we also don’t want them to wreck our stuff. So when we see them carrying our stuff, we quickly try to take it away from them.
And right here is where so many things happen that just make it all worse.
As humans, we are probably doing something else when our stuff gets grabbed. We might be working, eating, watching TV, or maybe reading. But when we notice that the dog has a Thing, our attention quickly shifts from whatever we were doing to the dog. If the dog likes having your eyes on them, the dog has just been reinforced for taking a Thing. AND THEN! We play a game of chase! So that’s fun too!! But we create a lot of conflict when we catch up to the dog. We might grab the collar, use an unpleasant tone of voice, pin them down, rip the item out of their mouth, manipulate their jaw, etc.
As difficult as it may be, it is almost always better to just ignore a dog that has stolen an item. Paying attention to it is likely to make that item feel more valuable. Instead, we might grab a more appropriate toy and make a big deal about how special it is, play with it by ourselves, and before you know it, the dog will probably decide that the appropriate toy is more valuable than the stolen item. This is, of course, so much easier when the stuff you really care about is put up out of reach of puppies and adolescent dogs.
—-
3. Now I’m going to talk about a mistake that I made. I was speaking at a 4H class. The library was so kind to let us have dogs in the basement. It was orientation night, and the children were not supposed to bring their dogs. I brought Mason to do some demos because he is excellent with people, and he is safe with dogs, but he is… loud. He’ll scream and scream and scream and scream if they can’t meet. It’s very off-putting, and it can be very scary if you don’t know him.
It was just my luck that one of the parents either didn’t see the e-mail or chose to ignore the instructions, and brought a tiny puppy. It was very small, and very cute. They hid it in their coat, and Mason made it through half of the class without realizing that another dog was there.
But I knew the dog was there, and I should have just brought him to my car and completed the lesson without a demo dog. But I thought “oh, if that puppy just stays in their coat, Mason will never know, and I can teach the lesson as planned.” Alas, the puppy did not stay in their coat.
I made three mistakes:
1.) I probably should not have brought Mason into a space that’s known for requiring quiet participation.
2.) I should not have trusted that parents and kids would abide by our rules.
3.) When I finally did learn about the dog that wasn’t supposed to be there, I should have brought Mason to the car before anything happened.
Of course, the tiny puppy woke up and wriggled out of the owner’s jacket. Mason saw A PUPPY and his brain melted out of his skull and he started screaming. Mason is safe, even mid-meltdown, but the whole performance is incredibly off-putting, extremely loud, and again, we were in a library.
A library worker came down when she heard Mason’s noise. She was quite frustrated with me, and she was understandably upset that this was happening. I was already trying to get Mason out of there. I ran into this library worker in the hallway as I was trying to get him out to my car. I was already leaving, but her need for control got in the way. She ended up delaying the outcome that she was looking for. I was already on my way out, but she still felt the need to stop me in the hallway. She kept telling me over and over and over and over that the dog needed to leave. I was nodding and agreeing, and just waiting for her to stop talking and move out of my way. She was blocking our escape with her body, and she just stood there scolding me, and I just kept nodding, and Mason just kept screaming.
That need for control… it’s a tough thing to balance. The library worker probably thought that she was protecting her patrons. In reality, she ended up prolonging the perceived risk to her patrons by exerting her authority in that situation. Wielding that that control was totally unhelpful in that situation.
—-
There are so many areas in animal training – and in life – where giving up a little control will actually give us more control, and make things safer, easier and more enjoyable. It sure is hard to do, but I’m working at it. I hope you’ll join me!